

半导体量子点中电子态的绝热捷径控制
收稿日期: 2020-12-26
网络出版日期: 2021-02-28
基金资助
国家自然科学基金资助项目(12075145);上海市科委基金资助项目(2019SHZDZX01-ZX04);上海市科委基金资助项目(18010500400);上海市科委基金资助项目(18ZR1415500);上海市高校特聘教授"东方学者"跟踪计划资助项目
Shortcuts to adiabatic control of electron states in semiconductor quantum dots
Received date: 2020-12-26
Online published: 2021-02-28
班玥, 李欣和, 陈玺 . 半导体量子点中电子态的绝热捷径控制[J]. 上海大学学报(自然科学版), 2021 , 27(1) : 1 -17 . DOI: 10.12066/j.issn.1007-2861.2273
Fast and accurate quantum state preparation and manipulation are important tasks in the field of quantum information processing and solid-state-based quantum computing. In recent years, shortcuts to adiabaticity have been widely used in atom cooling, transfer, and other quantum information processing, aiming to accelerate slow adiabatic processes. In this study, fast, robust control schemes for electron quantum states in different semiconductor quantum dot systems are reviewed using shortcuts to adiabaticity. The different methods include invariant-based inverse engineering and transitionless quantum driving. The various protocols and effects of environmental decoherence and other system factors on quantum state manipulation are analysed.
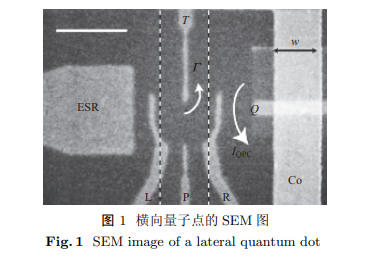
| [1] | Pioro-Ladrière M, Tokura Y, Obata T, et al. Spin-charge qubit resonance readout in lateral quantum dots[J]. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 2007,40(2):347-350. |
| [2] | Loss D, Divincenzo D P. Quantum computation with quantum dots[J]. Physical Review A, 1998,57(1):120. |
| [3] | Hanson R, Kouwenhoven L P, Petta J R, et al. Spins in few-electron quantum dots[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2007,79(4):1217. |
| [4] | Ladd T D, Jelezko F, Laflamme R, et al. Quantum computers[J]. Nature, 2010,464(7285):45-53. |
| [5] | Hayashi T, Fujisawa T, Cheong H D, et al. Coherent manipulation of electronic states in a double quantum dot[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003,91(22):226804. |
| [6] | Cao G, Li H O, Tu T, et al. Ultrafast universal quantum control of a quantum-dot charge qubit using Landau-Zener-Stückelberg interference[J]. Nature Communications, 2013,4(1):1-7. |
| [7] | Bluhm H, Foletti S, Neder I, et al. Dephasing time of GaAs electron-spin qubits coupled to a nuclear bath exceeding 200 $\mu$s[J]. Nature Physics, 2011,7(2):109-113. |
| [8] | Divincenzo D P. The physical implementation of quantum computation[J]. Fortschritte der Physik: Progress of Physics, 2000,48(9/10/11):771-783. |
| [9] | Petta J R, Johnson A C, Taylor J M, et al. Coherent manipulation of coupled electron spins in semiconductor quantum dots[J]. Science, 2005,309(5744):2180-2184. |
| [10] | Elzerman J M, Hanson R, van Beveren L H W, et al. Semiconductor few-electron quantum dots as spin qubits[M] // Heiss W D. Quantum dots: a doorway to nanoscale physics. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2005: 25-95. |
| [11] | Eriksson M A, Friesen M, Coppersmith S N, et al. Spin-based quantum dot quantum computing in silicon[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2004,3(1/2/3/4/5):133-146. |
| [12] | Kane B E. A silicon-based nuclear spin quantum computer[J]. Nature, 1998,393(6681):133-137. |
| [13] | Koppens F H L, Buizert C, Vink I T, et al. Detection of single electron spin resonance in a double quantum dot[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007,101(8):081706. |
| [14] | Sanada H, Kunihashi Y, Gotoh H, et al. Manipulation of mobile spin coherence using magnetic-field-free electron spin resonance[J]. Nature Physics, 2013,9(5):280-283. |
| [15] | Smirnov A I, Soldatov T A, Povarov K Y, et al. High-field magnetic resonance of spinons and magnons in the triangular lattice $S=1/2$ antiferromagnet Cs$_2$CuC$_{l4}$[J]. Physical Review B, 2015,91(17):174412. |
| [16] | San-Jose P, Scharfenberger B, Sch?n G, et al. Geometric phases in semiconductor spin qubits: manipulations and decoherence[J]. Physical Review B, 2008,77(4):045305. |
| [17] | Nadj-Perge S, Frolov S M, van Tilburg J W W, et al. Disentangling the effects of spin-orbit and hyperfine interactions on spin blockade[J]. Physical Review B, 2010,81(20):201305. |
| [18] | Nowack K C, Koppens F H L, Nazarov Y V, et al. Coherent control of a single spin with electric fields[J]. Science, 2007,318(5855):1430-1433. |
| [19] | Rashba E I, Efros A L. Orbital mechanisms of electron-spin manipulation by an electric field[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003,91(12):126405. |
| [20] | Engel H A, Rashba E I, Halperin B I. Theory of spin hall effects in semiconductors [EB/OL]. (2007-12-15) [2020-11-10]. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470022184.hmm508. |
| [21] | Li R, You J Q. Anisotropic exchange coupling in a nanowire double quantum dot with strong spin-orbit coupling[J]. Physical Review B, 2014,90(3):035303. |
| [22] | Coish W A, Loss D. Hyperfine interaction in a quantum dot: non-Markovian electron spin dynamics[J]. Physical Review B, 2004,70(19):195340. |
| [23] | Witzel W M, Sarma S D. Quantum theory for electron spin decoherence induced by nuclear spin dynamics in semiconductor quantum computer architectures: spectral diffusion of localized electron spins in the nuclear solid-state environment[J]. Physical Review B, 2006,74(3):035322. |
| [24] | Cywinski L, Witzel W M, Sarma S D. Electron spin dephasing due to hyperfine interactions with a nuclear spin bath[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009,102(5):057601. |
| [25] | Laird E A, Barthel C, Rashba E I, et al. Hyperfine-mediated gate-driven electron spin resonance[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007,99(24):246601. |
| [26] | Osika E N, Chacón A, Lewenstein M, et al. Spin-valley dynamics of electrically driven ambipolar carbon-nanotube quantum dots[J]. Journal of Physics Condensed Matter, 2017,29(28):285301. |
| [27] | Shafiei M, Nowack K C, Reichl C, et al. Resolving spin-orbit-and hyperfine-mediated electric dipole spin resonance in a quantum dot[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013,110(10):107601. |
| [28] | San-Jose P, Scharfenberger B, et al. Geometric phases in semiconductor spin qubits: manipulations and decoherence[J]. Physical Review B, 2008,77(4):045305. |
| [29] | Kawakami E, Scarlino P, Ward D R, et al. Electrical control of a long-lived spin qubit in a Si/SiGe quantum dot[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2014,9(9):666-670. |
| [30] | Liu R C, Odom B, Yamamoto Y, et al. Quantum interference in electron collision[J]. Nature, 1998,391(6664):263-265. |
| [31] | Press D, de Greve K, McMahon P L, et al. Ultrafast optical spin echo in a single quantum dot [J]. Nature Photonics, 2010,4(6):367-370. |
| [32] | Kim D, Ward D R, Simmons C B, et al. Microwave-driven coherent operation of a semiconductor quantum dot charge qubit[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015,10(3):243-247. |
| [33] | Ward D R, Kim D, Savage D E, et al. State-conditional coherent charge qubit oscillations in a Si/SiGe quadruple quantum dot[J]. NPJ Quantum Information, 2016,2(1):1-6. |
| [34] | Li H O, Cao G, Yu G D, et al. Conditional rotation of two strongly coupled semiconductor charge qubits[J]. Nature Communications, 2015,6(1):1-9. |
| [35] | Li H O, Cao G, Yu G D, et al. Controlled quantum operations of a semiconductor three-qubit system[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2018,9(2):024015. |
| [36] | Busl M, Granger G, Gaudreau L, et al. Bipolar spin blockade and coherent state superpositions in a triple quantum dot[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2013,8(4):261-265. |
| [37] | Sánchez R, Granger G, Gaudreau L, et al. Long-range spin transfer in triple quantum dots[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2014,112(17):176803. |
| [38] | Gallego-Marcos F, Sánchez R, Platero G. Coupled Landau-Zener-Stückelberg quantum dot interferometers[J]. Physical Review B, 2016,93(7):075424. |
| [39] | Gallego-Marcos F, Sánchez R, Platero G. Photon assisted long-range tunneling[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2015,117(11):112808. |
| [40] | Stano P, Klinovaja J, Braakman F R, et al. Fast long-distance control of spin qubits by photon-assisted cotunneling[J]. Physical Review B, 2015,92(7):075302. |
| [41] | Braakman F R, Barthelemy P, Reichl C, et al. Long-distance coherent coupling in a quantum dot array[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2013,8(6):432-437. |
| [42] | Greentree A D, Cole J H, Hamilton A R, et al. Coherent electronic transfer in quantum dot systems using adiabatic passage[J]. Physical Review B, 2004,70(23):235317. |
| [43] | Huneke J, Platero G, Kohler S. Steady-state coherent transfer by adiabatic passage[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013,110(3):036802. |
| [44] | Feng M K, Kwong C J, Koh T S, et al. Coherent transfer of singlet-triplet qubit states in an architecture of triple quantum dots[J]. Physical Review B, 2018,97(24):245428. |
| [45] | Baart T A, Jovanovic N, Reichl C, et al. Nanosecond-timescale spin transfer using individual electrons in a quadruple-quantum-dot device[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016,109(4):043101. |
| [46] | Delbecq M R, Nakajima T, Otsuka T, et al. Full control of quadruple quantum dot circuit charge states in the single electron regime[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014,104(18):183111. |
| [47] | Ito T, Otsuka T, Amaha S, et al. Detection and control of charge states in a quintuple quantum dot[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016,6(1):1-7. |
| [48] | Zajac D M, Hazard T M, Mi X, et al. Scalable gate architecture for a one-dimensional array of semiconductor spin qubits[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2016,6(5):054013. |
| [49] | Puddy R K, Smith L W, Al-Taie H, et al. Multiplexed charge-locking device for large arrays of quantum devices[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2015,107(14):143501. |
| [50] | Fujita T, Baart T A, Reichl C, et al. Coherent shuttle of electron-spin states[J]. NPJ Quantum Information, 2017,3(1):1-6. |
| [51] | Noiri A, Nakajima T, Yoneda J, et al. A fast quantum interface between different spin qubit encodings[J]. Nature Communications, 2018,9(1):1-7. |
| [52] | Mills A R, Zajac D M, Gullans M J, et al. Shuttling a single charge across a one-dimensional array of silicon quantum dots[J]. Nature Communications, 2019,10(1):1-6. |
| [53] | Sarandy M S, Lidar D A. Adiabatic approximation in open quantum systems[J]. Physical Review A, 2005,71(1):012331. |
| [54] | Bergmann K, Theuer H, Shore B W. Coherent population transfer among quantum states of atoms and molecules[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1998,70(3):1003-1025. |
| [55] | Leanhardt A E, Pasquini T A, Saba M, et al. Cooling Bose-Einstein condensates below 500 picokelvin[J]. Science, 2003,301(5639):1513-1515. |
| [56] | Shafiei M, Nowack K C, Reichl C, et al. Resolving spin-orbit-and hyperfine-mediated electric dipole spin resonance in a quantum dot[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013,110(10):107601. |
| [57] | Chen X, Lizuain I, Ruschhaupt A, et al. Shortcut to adiabatic passage in two-and three-level atoms[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2010,105(12):123003. |
| [58] | Chen X, Ruschhaupt A, Schmidt S, et al. Fast optimal frictionless atom cooling in harmonic traps: shortcut to adiabaticity[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2010,104(6):063002. |
| [59] | Ibá?ez S, Chen X, Torrontegui E, et al. Multiple Schr?dinger pictures and dynamics in shortcuts to adiabaticity[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012,109(10):100403. |
| [60] | Torrontegui E, Ibánez S, Chen X, et al. Fast atomic transport without vibrational heating[J]. Physical Review A, 2011,83(1):013415. |
| [61] | Li Y, Wu L A, Wang Y D, et al. Nondeterministic ultrafast ground-state cooling of a mechanical resonator[J]. Physical Review B, 2011,84(9):094502. |
| [62] | Zhang J Q, Li Y, Feng M. Cooling a charged mechanical resonator with time-dependent bias gate voltages[J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 2013,25(14):142201. |
| [63] | Bason M G, Viteau M, Malossi N, et al. High-fidelity quantum driving[J]. Nature Physics, 2012,8(2):147-152. |
| [64] | Yuce C. Fast frictionless expansion of an optical lattice[J]. Physics Letters A, 2012,376(21):1717-1720. |
| [65] | Faure S, Ciliberto S, Trizac E, et al. Shortcut to stationary regimes: a simple experimental demonstration[J]. American Journal of Physics, 2019,87(2):125-129. |
| [66] | Yu X T, Zhang Q, Ban Y, et al. Fast and robust control of two interacting spins[J]. Physical Review A, 2018,97(6):062317. |
| [67] | Chen X, Jiang R L, Li J, et al. Inverse engineering for fast transport and spin control of spin-orbit-coupled Bose-Einstein condensates in moving harmonic traps[J]. Physical Review A, 2018,97(1):013631. |
| [68] | Chen X, Li H, Sun S, et al. Effect of hydrothermal pretreatment on the structural changes of alkaline ethanol lignin from wheat straw[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016,6(1):1-9. |
| [69] | Berry M V. Transitionless quantum driving[J]. Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical, 2009,42(36):365303. |
| [70] | Chen X, Muga J G. Engineering of fast population transfer in three-level systems[J]. Physical Review A, 2012,86(3):033405. |
| [71] | Ban Y, Chen X, Platero G. Fast long-range charge transfer in quantum dot arrays[J]. Nanotechnology, 2018,29(50):505201. |
| [72] | Ban Y, Chen X. Counter-diabatic driving for fast spin control in a two-electron double quantum dot[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014,4:6258. |
| [73] | Baksic A, Ribeiro H, Clerk A A. Speeding up adiabatic quantum state transfer by using dressed states[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2016,116(23):230503. |
| [74] | Ban Y, Jiang L X, Li Y C, et al. Fast creation and transfer of coherence in triple quantum dots by using shortcuts to adiabaticity[J]. Optics Express, 2018,26(24):31137-31149. |
| [75] | Ban Y, Chen X, Sherman E Y, et al. Fast and robust spin manipulation in a quantum dot by electric fields[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012,109(20):206602. |
| [76] | Ban Y, Chen X, Muga J G, et al. Fast spin control in a two-electron double quantum dot by dynamical invariants [EB/OL]. (2013-09-07)[2020-12-26]. https:/arXiv.org/abs/1309.1916v1. |
| [77] | Ban Y, Chen X, Kohler S, et al. Spin entangled state transfer in quantum dot arrays: coherent adiabatic and speed-up protocols[J]. Advanced Quantum Technologies, 2019,2(10):1900048. |
| [78] | Masuda S, Tan K Y, Nakahara M. Spin-selective electron transfer in a quantum dot array[J]. Physical Review B, 2018,97(4):045418. |
| [79] | L?wdin P O. A note on the quantum-mechanical perturbation theory[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1951,19(11):1396-1401. |
| [80] | Bergmann K, Theuer H, Shore B W. Coherent population transfer among quantum states of atoms and molecules[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1998,70(3):1003-1025. |
| [81] | Malinovsky V S, Tannor D J. Simple and robust extension of the stimulated Raman adiabatic passage technique to $N$-level systems[J]. Physical Review A, 1997,56(6):4929. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |